Logic
Logic blocks can perform different operations based on the condition of mathematical or logical expressions.
The following logic blocks execute an operation depending on the result of a condition. Set the [If] or [If Else] condition in a value block or logic block.
The following logic blocks output numerical or logical values for use in conditions.
- When one of the following occurs in the value of an operand, the value is undefined:
Communication error (variable has "bad" quality)
Accessing array element number that is out of bounds
Divide by zero.
If the logic block contains undefined values, the result is undefined. However, when used as a [Logical Condition], it may still output a result.
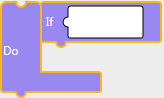
If
This block executes operations under the [Do] when [If] condition evaluates to true.Block
Text
'if(CONDITION){}'
During execution of the script, if the [If] condition is undefined, exits the block.
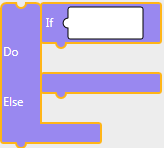
If Else
This block executes operations under the [Do] when [If] condition evaluates to true, and operations under the [Else], when [If] condition evaluates to false.Block
Text
'if(CONDITION){}else{}'
During execution of the script, if the [If] condition is undefined, logic skips [Do] and executes the [Else] operation.
Math
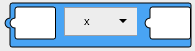
This block is mathematical expression. Insert the value block in left operand (X) and right operand (Y), and select the operator.Block
Text
'SOURCE1 * SOURCE2'
Operator |
Expression |
Description |
| + | X + Y | Add |
| - | X - Y | Subtract |
| * | X * Y | Multiply |
| / | X / Y | Divide |
| % | X % Y | Remainder of division |
| & | X & Y | Returns the result of the AND operation at the bit level. If X = 0110; Y= 1100 then the result is 0100 |
| | | X | Y | Returns the result of the OR operation at the bit level. If X = 0110; Y= 1100 then the result is 1110 |
| ^ | X ^ Y | Returns the result of the XOR operation at the bit level. If X = 0110; Y= 1100 then the result is 1010 |
| << | X << Y | Left shift. Shifts the bits in X, to the left, by the Y number of bit positions. Preserves the sign. |
| >> | X >> Y | Right shift. Shifts the bits in X, to the right, by the Y number of bit positions. Preserves the sign. |
| >>> | X >>> Y | Zero fill, right shift. Shifts the bits in X, to the right, by the Y number of bit positions, and fills in shifted bits on the left with 0s, thereby not preserving the sign. |
- AND/OR/XOR always return a 32 bit unsigned integer value.
- When the input value is negative, bit shift expressions return a 32 bit integer value.
- When the input value is positive, bit shift expressions return a 32 bit unsigned integer value.
The mathematical expression result contains decimal points.
(Example 1)
In the following case, if the value of INT1
is 101, then the result is 10.1 (.1 is not truncated).
Block

Text
'INT1 / 10'
To truncate the decimal points, use the floor
block.
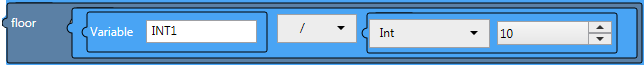
(Example 2)
In the following case, if the value of INT1
is 101, then the result is 10.
Block
Text
'$Math.floor((INT1 / 10))'
Comparison Condition
This block is comparison condition. Insert a value block in the left operand (X) and the right operand (Y) and select an operator.
Block
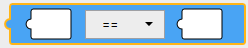
Text
'CONDITION1 == CONDITION2'
Operator |
Description |
Example |
<= |
Returns true if the value of X is less than or equal to the value of Y. |
If X = 7 and Y = 33, then the expression X <= Y is true. |
>= |
Returns true if the value of X is greater than or equal to the value of Y. |
If X = 32 and Y = 10, then the expression X >= Y is true. |
| < | Returns true if the value of X is less than the value of Y. |
If X = 7 and Y = 38, then the expression X < Y is true. |
| > | Returns true if the value of X is greater than the value of Y. |
If X = 27 and Y = 14, then the expression X > Y is true. |
| != | Returns true if the value of X is not equal to the value of Y. |
If X = 7 and Y = 33, then the expression X != Y is true. |
| == | Returns true if the value of X is equal to the value of Y. |
If X = 5 and Y = 5, then the expression X == Y is true. |
Logical Condition
This block is logical condition. Insert a value block in the left operand (X) and the right operand (Y) and select an operator.
Block
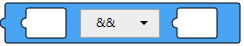
Text
'CONDITION1 && CONDITION2'
| Operator | Description |
Example | ||||||||||||||||||
| && | Logical AND Returns true if both are true. |
If X
= true, Y
= false, then the expression X
&& Y
is false.
Even though the value of one of the operands may be undefined, the resulting logical condition could evaluate to false if the other operand is false. Please see table below.
|
||||||||||||||||||
| || | Logical Sum Returns true except if both the inputs are false. |
If X
= true, Y
= false, then the expression X
|| Y
is true.
Even though the value of one of the operands may be undefined, the resulting logical condition could evaluate to true if the other operand is true. Please see table below.
|
Not
This block performs logical negation or bit negation. Insert a value block in the operand (X) and select an operator.
Block
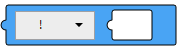
Text
'!SOURCE'
| Operator | Description |
Example |
| ! | Logical NOT Returns the inverse of the boolean value. |
If X = false, then the result is true. |
| ˜ | Bit NOT Returns the inverse value of each bit. When using integers, the bit length of bit expressions is always 32 bits. |
If X = 0011, then the result is 1100. |